Abortion Access: Europe v.s the United States
Since the repeal of Roe v. Wade and the subsequent criminalization and ban on abortion across several US States, reproductive autonomy and medical safety have been top of mind for many Americans. Our top priority at Skola is to help you make a well-informed decision about your degree and life abroad. Understanding how your reproductive rights will be affected based on the country you choose is essential, especially for women and people capable of pregnancy.
Below is an overview of the types of laws on abortion protection in Europe, along with a comparison to those in the US, to provide context for Americans and to illustrate how laws differ.
Note: This article presents a broad overview of abortion laws and protections across Europe (EU, UK, and neighboring countries) in comparison to the US. Please keep in mind that legislation, as well as the social and political situations in all locations, are complex and highly nuanced. This overview is designed for prospective international students to gain a basic understanding of abortion protection in various countries. Sources and resources for further reading are linked at the bottom.
Trigger Warning: This article includes mentions of sexual assault and violence.
Source: Gayatri Malhotra via Unsplash
Levels of Protection
Several types of abortion legislation exist and are categorized into a few broad levels. Some of these key terms are defined below to help you quickly understand the graphics that follow.
-
The right of a pregnant person to have an abortion solely at their own request.
Doctors are not required to approve the patient’s decision or certify that specific conditions exist, such as a sexual assault, health risks, or certain social circumstances. (The Center for Reproductive Rights)
The amount of time a patient has to receive an abortion differs from country to country. In most of Europe, the gestational limit falls between 10 and 14 weeks. The gestational limit increases to 18 weeks or more in the Netherlands, Sweden, Denmark, Norway, and Iceland.
In the United States, an abortion on request is often discussed in the context of elective abortions, in which an abortion is performed for reasons other than a direct, immediate threat to maternal physical health.
Abortion available on request is considered the global best practice.
-
Abortion is permitted under a broad range of circumstances, considering the potential impact of pregnancy and giving birth, and taking into account a pregnant person's environment and their social or economic circumstances.
-
Abortion is permitted when the pregnancy poses a health risk.
Some countries’ laws may extend authorization to the preservation of mental health, while others strictly permit abortion only when the patient's physical health is threatened.
-
Abortion is only permitted when the pregnant person’s life is at risk.
-
Abortion is completely banned. It is not permitted under any circumstances, including when the person’s life or health is at risk.
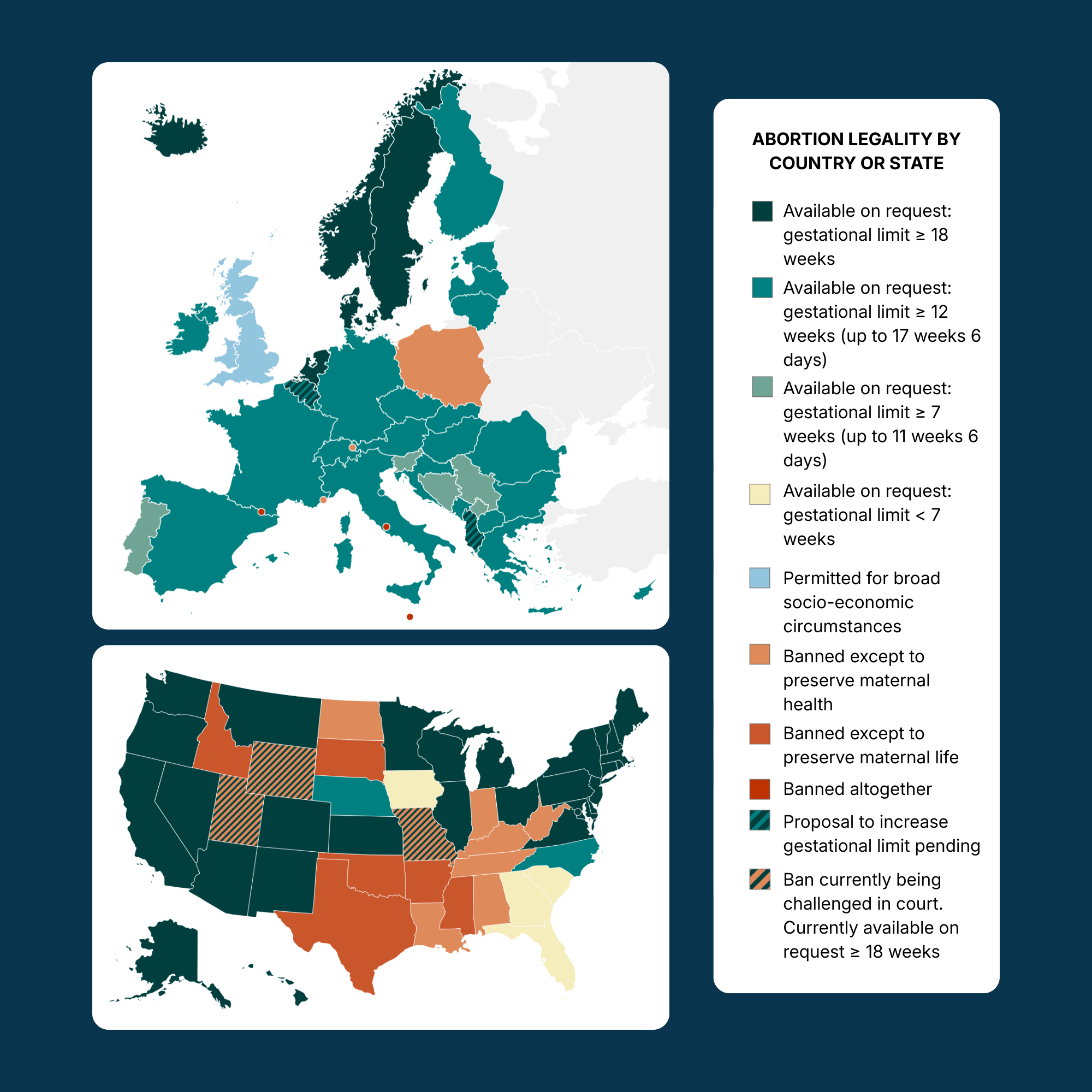
Comparing the US & Europe
Sources Europe: Center for Reproductive Rights, European Parliamentary Forum for Sexual & Reproductive Rights
Sources USA: KFF, Center for Reproductive Rights, Power to Decide Abortion Finder
Abortion in Europe
Standard Practice
Across Europe, the standard practice is to permit abortion on request for at least the first trimester of pregnancy (12 weeks). The gestational limit is typically increased to 18 weeks in cases such as rape, sexual violence, incest, medical necessity, fetal diagnosis, or even socio-economic circumstances. There are no time limits when there is a risk to the pregnant person’s health or life.
England, Scotland, and Wales do not follow the standard practice of abortion on request. In these countries, abortion is permitted on broad socio-economic grounds. However, the way the law is interpreted, abortion is highly accessible across the UK and wouldn’t be considered to be under any ban.
Abortion Bans in Europe
Poland and Malta are the only EU countries with abortion bans in place. In Poland, abortion is only permitted for risks to the health or life of a pregnant person. Malta permits abortion only when there is a risk to life.
Andorra, Liechtenstein, Monaco, and Vatican City also ban abortion. These sovereign microstates are catholic monarchies and are not members of the EU.
Medical Necessity
Every country in the EU and the UK permits abortions when the pregnant person’s health or life is at risk. “Health” is often interpreted broadly, extending to both physical and mental health risks. Under these circumstances, abortion is typically permitted until 18 weeks. In cases of a serious health or life-threatening risk to the patient, most countries do not impose any time limit.
Cost of Abortion in Europe
In most EU countries and the whole UK, abortion is free or nearly free for citizens and non-citizen residents under their national health systems. In a few EU countries, there is limited conditional coverage, or it is free only in certain circumstances.
For international students in Europe, as non-citizen residents, the cost of health insurance ranges from €5 to €120 ($6-$140) per month, with most countries falling into the range of about €30 to €50 ($35-$58).
On the low end, in Belgium, student health insurance ranges from free to €20 ($23) per month based on your income. With health insurance, an abortion has a copay of €3.90 ($4.59). (VUB)
In the Netherlands, abortion is free under the Long-term Care Act (Wet Langdurige Zorg, WLZ). However, foreign students are not included in this fund. As a result, most international students must pay out of pocket for an abortion. Costs range from under €100 (pill) to €1,500 (surgical), depending on the method and stage. (Women on Waves)
Abortion in the US
Standard Practice
Abortion law is heavily divided in the US.
In states where abortion is legal, the standard practice is to legalize abortion until fetal viability (generally considered to be at 22-24 weeks). As in Europe, there are typically no time limits when there is a risk to the pregnant person’s health or life.
In states with bans, abortion tends to be highly restrictive, with exceptions only made for the health and/or life of the pregnant person.
Since the repeal of Roe v Wade, abortion legislation has been rapidly changing across the country.
Abortion Bans in the US
There are 13 US states with highly restrictive abortion bans in place. Another 4 states permit abortion on request only within extremely short gestational time limits, thus creating de facto bans. Bans are currently being challenged in court in 3 additional states.
7 of these states permit abortion only when the pregnant person’s health or life is at risk. In the 6 states with the most restrictive bans in place, abortion is only permitted in life-threatening circumstances.
Medical Necessity
In 44 states, abortion is permitted when the patient’s health is at risk. Every US state permits abortion when the patient’s life is at risk. In nearly all states with health exceptions to their bans, “health” is strictly limited to physical health. (KFF)
In states without bans in place, abortion is typically permitted after fetal viability to preserve the life or health of the pregnant person. In 11 of these states, “health” is defined as both physical and mental health. (Abortionfinder.org)
Cost of Abortion
In the US, federal funding for abortion is banned under the Hyde Amendment of 1977, with exceptions for pregnancies that endanger the life of the woman, or result from rape or incest.
On the state level, 31 states impose further limitations on Medicaid, private, and/or marketplace insurance coverage for abortions. On the other hand, 12 states require Medicaid, private insurance, and ACA marketplace plans to cover abortion. Of these, 9 states prohibit cost-sharing for abortion, making treatment free with insurance. (KFF)
According to Planned Parenthood, the average cost of a medication abortion in the first trimester is about $580. After the 12-week mark, the price increases; early in the second trimester, the average cost is $715, and by the end of the second trimester, it can cost between $1,500 - $2,000. Prices differ based on state and insurance coverage. (Planned Parenthood)
Recent Changes in European Legislation
Across the vast majority of the European Union and the United Kingdom, abortion is legal and protected, especially when it comes to the health and life of the pregnant person. Although a few conservative-leaning countries, such as Poland and Hungary, have followed the US’s lead in restricting abortion, many more countries have added additional protections and expanded access to abortion, including Belgium, Finland, the Netherlands, and more.
As of December 17, 2025, the European Parliament voted in support of an EU fund to expand access to abortion for people who can’t access an abortion in their own country. This new fund helps patients who must travel to another EU country to receive care.
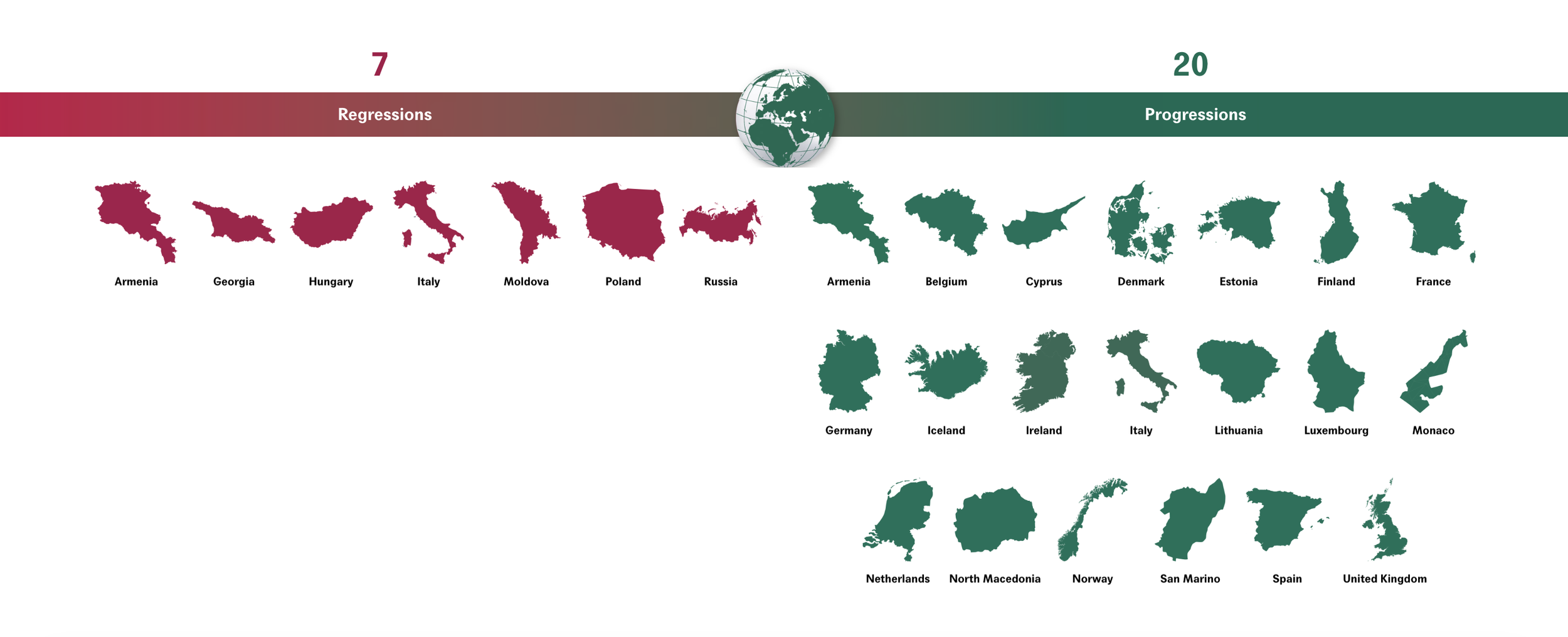
“In the last decade, 20 countries have taken progressive steps to expand access to abortion care by removing restrictions. In contrast, 7 countries have introduced regressive measures that create new barriers to access. Poland is the only country in Europe, and one of only 4 countries globally, to have removed a ground for legal abortion from its laws in the past 30 years.” Graphic and caption source: Center for Reproductive Rights, Abortion Laws in Europe 2025
Global Landscape on Abortion Access
Source : Center for reproductive rights via Focus 2030
In the graphic above, the United States does not fall into any category because there is no federal right to an abortion. However, according to the Center for Reproductive Rights, which created this map, the “laws currently being passed in the U.S. more closely resemble restrictions in highly restrictive countries like Uganda, Tanzania, Brazil, and Guatemala.”
Sources & Further Reading
Helpful Resources
Understanding Abortion Laws in Europe:
European Abortion Policy Atlas 2025
Center for Reproductive Rights: Abortion Laws in Europe
Abortion Access Help & Funds for International Students in Europe:
Belgium: VUB Dilemma
Czech Republic: Abortion Support Alliance Prague
France: Ministry of Health | Abortion Information Guide
Italy: Libera Di Abortire | Abortion in Italy Guide & Laiga | Map of Italian hospitals that offer abortion services
Malta: Family Planning Advisory Service (FPAS)
Netherlands: Women on Waves
Poland: Abortion without Borders
Spain: L'Associació de Drets Sexuals i Reproductius
Sources on Abortion in Europe
Center for Reproductive Rights | Abortion Laws in Europe
EPF for Sexual and Reproductive Rights | European Abortion Policy Atlas 2025
Politico | Europe votes to expand abortion access in historic ballot
Foundation for European Progressive Studies | Abortion in the EU - Country Factsheets (2023)
Center for Reproductive Rights | European Abortion Laws: a Comparative Overview (2022)
World Health Organization | Global Abortion Policies Database
Focus 2030 | Where do abortion rights stand in the world in 2024?
Council on Foreign Relations | Abortion Law: Global Comparisons
Sources on Abortion in the US
Center for Reproductive Rights | After Roe Fell: U.S. Abortion Laws by State
KFF | Dobbs-era Abortion Bans and Restrictions: Early Insights about Implications for Pregnancy Loss
KFF | How State Policies Shape Access to Abortion Coverage
Abortion Finder | State-by-State Guide